A couple decades ago, back in 1992, W. Warner Burke and George Litwan collated a number of organizational change models into one holistic view of how organizational structure and design affects change. With this research, Burke and Litwan developed the Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change, otherwise known as the Burke-Litwin Model.
Their seminal framework achieves 2 things: First, it identifies 12 factors of change. Note that this model is more comprehensive than the popularly used McKinsey 7-S organizational design model, which only captures 7 factors.
Secondly, it determines that there are certain consistent causal linkages among classes of events.
This model can be leveraged for the following purposes:
- Analyze Organizational Change
- Understand Organizational Change
- Manage Organizational Change
- Predict Organizational Change
It is important to recognize that even Burke and Litwan acknowledge this model is inherently imperfect, as every element affects every other. However, it is an attempt to provide hierarchy and identify strongest causal relationships, which will provide a deeper understanding of what and how change is driven in an organization.
The Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change is based on opens system theory, which states that all change in an organization stems from external influences. In open systems theory, there are 3 distinct elements:
- Input - The effect of the external environment on an organization.
- Output - Includes everything that happens within the organization.
- Throughput - Refers to what the organization produces.
The Throughput element can be further refined into top-level Transformational factors and day-to-day Transactional factors.
The 12 elements are identified as follows:
- Input and Output Elements:
- External Environment
- Individual and Organizational Performance
These two represent the input and the output elements of the open systems theory. External factors cause change in the organization and the throughput produces performance. Note that Performance and the Environment affect each other equally—e.g., quality of products affecting customer satisfaction, improved sustainability affecting company reputation.
- Throughput > Transformational Elements:
- Leadership
- Mission and Strategy
- Organizational Culture
These transformational elements are those deeply embedded within an organization, which require top-level, revolutionary measures to change (i.e. organizational "transformation" initiatives). These elements should be the responsibility of organizational leaders, rather than managers.
- Throughput > Transactional Elements:
- Management Practices
- Structure
- Systems (Policies and Procedures)
- Work Unit Climate
- Motivation
- Task Requirements and Individual Skills/Abilities
- Individual Needs and Values
The transactional elements deal more with the day-to-day operation of the organization, rather than the big picture. While they do affect transformational factors, transactional factors are more strongly affected by transformational ones. These are the under responsibility of managers (not leadership).
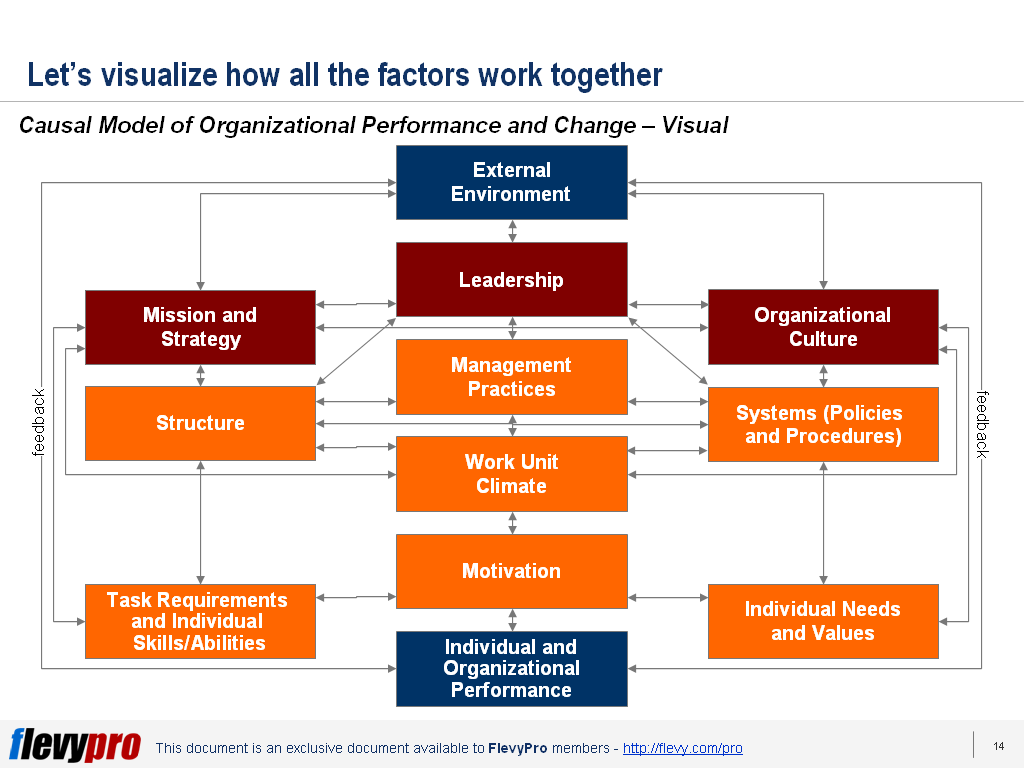
And now, for the big unveil... Visually, this diagram below depicts how the 12 elements fit together in our the Burke-Litwin Change Model.
Note how when we look at the full model, there is a hierarchical structure with a logical flow of influence from one factor to the next.
For instance, focusing on the central spine, it is evident that a change in the External Environment could cause the Leadership to make changes to management practices. This change would affect the Work Unit Climate, which could directly affect Motivation, thereby influencing Performance.
If we evaluate the grouping at the bottom of the model, the Work Unit Climate, Task Requirements and Individual Skills, and Individual Needs and Values are the elements that have the most direct effect on Motivation.
The Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change is powerful tool for understanding and driving organizational change, though it does have its limitations. Foremost, critics feel the model is a bit complex. Secondly, there are organizational changes that may be initiated by leadership or by internal factors rather, than by the external environment.
What are your thoughts on this Change and Transformation framework?
You can download an editable PowerPoint about the Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Comments