Organizations across all industries are undertaking “digital transformation” projects. But, what exactly is it? And, are they doing it right?
At it’s core, Digital Transformation is driven by the tangible shift in the role of the technology within an organization. No longer as purely a support function that enables business processes, technology is now capable of much more. Technology now allows for new, innovative business models (e.g. XaaS), drives sales growth, and can even be a source of competitive advantage.
This has all become possible due to 6 core emerging technologies:
- Social Media
- Mobility
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Cybersecurity
- Big Data
- Cloud
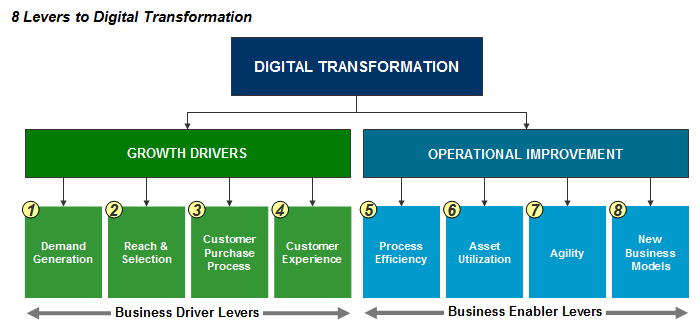
With these technology trends, businesses are armed with the capability to fully digitize, transform, and grow their organizations. These technologies, in fact, mobilize 8 levers to Digital Transformation–spanning both Growth (business drivers) and Operational Improvement (business enablers). These 8 levers are listed and depicted in the diagram below.
Only after we understand the levers to Digital Transformation, can we properly formulate our Digital Transformation Strategy.
1. Demand Generation
Emerging technologies, particularly social media (and social media marketing), are facilitating Demand Generation by building awareness and brand interest.
With an increasing number of customer touch points and ability to collect and unify customer data across these various touch points, we are better able to understand our customers and their interests—leading towards customer “micro-segmentation.”
Likewise, advertising platforms (as they, too, are collecting more and more customer data) also allow for more targeted ads. You can reach consumers by demographics, behavior, location, and so forth.
2. Search & Selection
We can now be where customers can easily find us—and likewise, can easily find customers wherever they may be. This has been largely made possible through Mobile and Internet technologies.
This includes across channels (online and offline), across devices (e.g. PC, mobile), and across platforms (e.g. website, search, email, social). GPS and location-based services allow us to find customers based on where they are and where they have been.
3. Customer Experience
Prior to the Internet era, customers had limited interactions with a company—e.g., retail salesman, telephone customer service. With emerging technologies—namely, Social Media, Mobility, Internet of Things—the number of customer touch points has increased dramatically. This is both an increase in number of ways for the customer to reach company and an increase to the number of people within a company to reach the customer. Companies now have the ability to constantly engage with the customer.
Thus, Customer Experience has grown in an increasing importance. In fact, growth tends to come through Customer Experiences and relationships that adapt to their dynamics and demands.
Information is at the center of the transformed “digital” business model. Information is usually the basis for differentiating Customer Experiences. Personalization is critical to an improved experience for the customer.
4. Customer Purchase Process
As Customer Experience has evolved through an increase in touch points and personalization, naturally, so has the Customer Purchase Process. Customers can be reach now with:
- New and optimized products and services
- New and optimized channels
- New pricing models
Likewise, existing channels, services, and products can also be improved and better leveraged.
As we can better target customers and tailor our offerings, customer profitability (or revenue per customer) is a metric that should see considerable improvement. Technology also shortens product development cycles and reduces the time to market for offerings.
5-8. Operational Improvement Levers
Operational improvement can be achieved through new combinations of information, processes, channels, and workforce abilities that leverage new, high-performance business and operating models. In our framework, we’ve broken down the levers as:
- Process Efficiency
- Asset Utilization
- Agility
- New Business & Service Models
It is important to realize that we may not be able to realize digital ambitions if we are tied down by the cost, complexity, and limited capacity of legacy systems. Companies are increasingly reducing costs to further invest in a unified digital infrastructure. A digital business platform supports a diverse set of customer and operational requirements with a single set of resources.
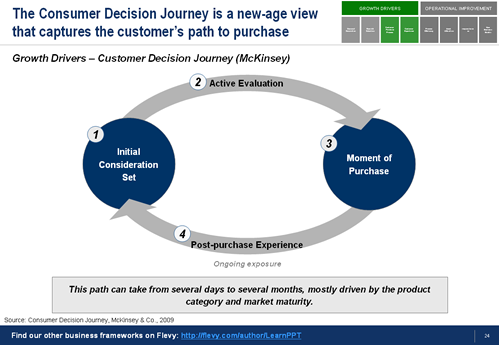
Of these 8 levers, Customer Experience is at the core of Digital Transformation-driven growth. Customer Experience has evolved from a traditional linear process (with few touch points) to a continuous, circular process (with constant touch points).
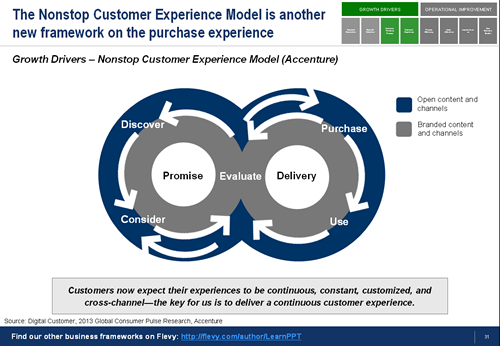
This change in Customer Experience is so significant that many top management consulting firms have developed their own frameworks addressing this behavioral and operational change, such as McKinsey’s Customer Decision Journey and Accenture’s Nonstop Customer Experience Model (see framework visuals below).
Today’s customer journey is dynamic, accessible, and continuous, because the digital touch points consumers are exposed to are always on and customers can constantly re-evaluate their purchase options. Enabled by technology, customers expect to easily control and vary their routes within and across channels to suit their needs at any given moment. Customers now expect their experiences to be continuous, constant, customized, and cross-channel.
The key, then, is for us to deliver a continuous customer experience. Otherwise, in today’s “switching economy,” a customer may quickly look for a different provider that does provide the continuous experience she desires.
The shift in technology was the catalyst to Digital Transformation. The shift in customerbehavior and experience was the outcome. Now, for a successful Digital Transformation Strategy, management must also have a shift in thinking.
Conventional strategy is no longer the best fit for meeting the demands of digital growth. A Digital Strategy mindset provides a guide for future growth.
Given the rapid rate and large magnitude of digital change, traditional annual strategic planning cycles are challenged when required to assess the new needs and appropriately redeploy resources. An effective digital business strategy uses new approaches to increasing strategic agility by generating early experience and reincorporating such experience into learning through the strategy process.
Each member of management must change his or her thinking appropriately. With the availability of more and better information, leadership should demand capabilities that are much more responsive to shifting marketing conditions. In formulating our Digital Transformation Strategy, we need to determine how and what information can be shared across the organization–across multiple levers–to maximize both growth and efficiency gains.
What are your thoughts on this approach to Digital Transformation Strategy?
You can download an editable PowerPoint about the Digital Transformation Strategy here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Comments
Dear David, I agree with you to some extent. I think " Human Side" has a great influence in each 8 levers . I suppose that we cannot achieve the target of digital transformation without define the the human side impact very precisely.
Thanks. Extremely clear.