A commonly quoted statistic is that 80% to 95% of the cost of a product is determined by its design and is therefore set before the item enters manufacturing. This assumption suggests that the dominant focus of Cost Management should be during Product Development and not during Manufacturing.
enters manufacturing. This assumption suggests that the dominant focus of Cost Management should be during Product Development and not during Manufacturing.
However, contrary to a widely held assumption, companies can integrate a variety of Cost Management techniques not only in the design phase but throughout the product life cycle. This is to ensure that there is a substantial reduction in costs. In fact, companies achieving Operational Excellence and competing aggressively on cost might consider the adoption of some form of an Integrated Cost Management Program that spans the entire product life cycle.
An organization must have a good understanding of Integrated Cost Management and the 5 Cost Management Strategies that they can use to reduce costs but still attain the desired level of functionality and quality at the target costs.
The 5 Cost Management Strategies
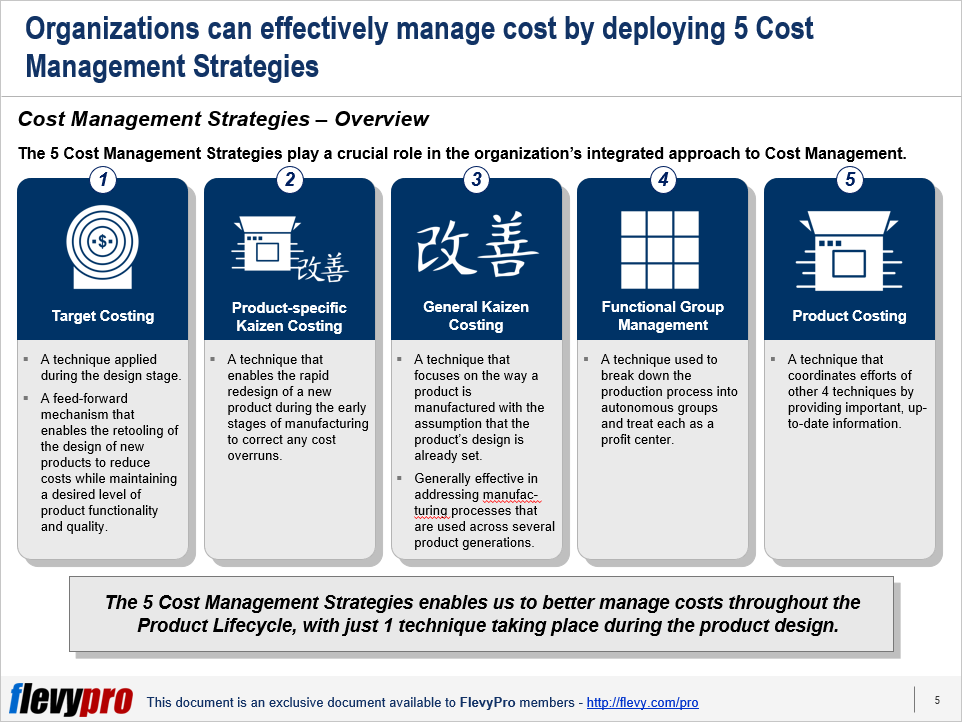
The 5 Cost Management Strategies play a crucial role in the company’s integrated approach to Cost Management.
The 5 Cost Management Strategies can be applied throughout the product life cycle with one technique used during the product design and the rest during manufacturing.
- Target Costing. This is a technique applied during the design stage. Target Costing is best used when the manufacturing phase of the life cycle of a product is short.
- Product-specific Kaizen Costing. This is a technique applied during the early stages of the manufacturing phase. It enables the rapid redesign of a new product to correct for any cost overruns. The primary rule in Product-specific Kaizen Costing is that the product’s functionality and quality have to remain constant.
- General Kaizen Costing. The third Cost Management Strategy, this technique is applied during the manufacturing phase. It focuses on the way a product is manufactured with the assumption that the product’s design is already set. This technique is effective when addressing manufacturing processes that are used across several product generations.
- Functional Group Management. This is the technique that is applied in the production process. Functional Group Management consists of breaking the production process into autonomous groups and treating each group as a profit instead of a cost center. The switch to profit as opposed to cost allows groups to increase the throughput of production processes even if changes result in higher costs. It enables the change in mindset that functional group management induces.
- Product Costing. The 5th Cost Management Strategy, this is the technique that coordinates the efforts of the other four techniques. It does coordination work by providing the other four techniques with important, up-to-date information.
Target Costing vis-a-vis Kaizen Costing
Kaizen Costing as known as continuous improvement costing. It is a method of reducing managing costs. Kaizen Costing has a similarity with Target Costing but it also has its differences. (Note: Kaizen is the Japanese term for Continuous Improvement and often tied to the philosophy of Lean Management.)
Both Kaizen Costing and Target Costing can achieve results with lower resources. This is basically their similarity. On the other hand, the differences lie in their usage and involvement.
Target Costing is used on the design stage and requires the involvement only of designers. On the other hand, Kaizen Costing is used during the manufacturing stage and requires high involvement of employees. The general idea of Kaizen Costing is to determine target costs, design products, and process to not exceed those costs.
Interested in gaining more understanding of these Cost Management Strategies? You can learn more and download an editable PowerPoint about 5 Cost Management Strategies here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Are you a management consultant?
You can download this and hundreds of other consulting frameworks and consulting training guides from the FlevyPro library.
Comments