As the last decisive step in customer service, a warehouse ensures cost effective distribution. Latest technological innovation has turned warehousing into a competitive advantage. It offers untapped potential for improvement. However, warehousing is a hugely neglected part of global supply chains. There is inconsistency in picking, packing and shipping orders, storing receipts, and managing inventory and logistics operations.
These and the following roadblocks in the way of smooth warehousing operations and Lean Management exist in every traditional warehouse:
- Lack of focus on acquiring technology to facilitate in improving efficiency and quality.
- Inability to utilize a structured approach to ascertain the reasons for poor performance.
- Lack of a big picture viewpoint pertaining to processes, costs, or external supply chain partnerships.
- Absence of a continuous improvement culture to achieve warehouse operations excellence.
- Lack of communication, organization, and proper training of resources.
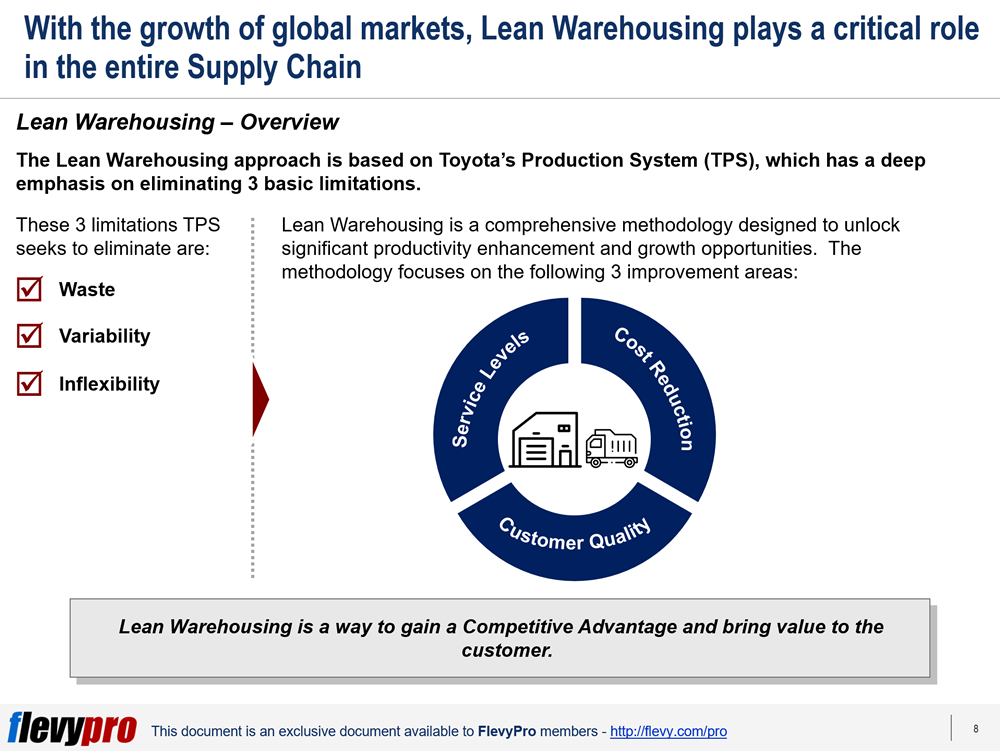
These shortcomings call for implementing Lean Warehousing methodology to unlock improvement opportunities and savings in operational, efficiency, and maintenance related costs. First initiated by Toyota, the Lean Warehousing approach has a deep emphasis on eliminating 3 basic limitations: waste, variability, and inflexibility. The Lean Warehousing methodology focuses on the following 3 improvement areas:
- Cost Reduction
- Customer Quality
- Service Levels
Cost Reduction
The Lean Warehousing methodology concentrates on increasing productivity and reducing operating costs. This is achieved by:
- Cutting undue walking and searching
- Preventing needless replenishment, reworks, waiting times, and double handling
- Upgrading demand and capacity planning and manpower allocation
Customer Quality
A Lean Warehouse seeks to take the customer quality to the next level by avoiding:
- Order deviations
- Picking errors
- Damaged goods
Service Levels
Improving service levels is at the center of a Lean Warehousing methodology, which involves:
- Reducing lead times
- Enhancing on-shelf availability
Lean Warehousing Transformation
Lean Warehousing Transformation entails streamlining operations to identify waste, know how to increase service levels, implement standardization and innovative ideas, and learn to evaluate and manage performance. Such transformation becomes a reality in an experiential learning environment and by developing organizational capabilities in 3 critical areas:
- Operating System
- Management Infrastructure
- Mindset and Behaviors
Operating System
The organizational capability to configure and optimize all company physical assets and resources to create value and minimize losses. The focus areas under operating systems include eradicating variability, encouraging flexibility, and promoting end-to-end design.
Management Infrastructure
The organizational capability to strengthen formal structures, processes, and systems necessary to manage the operating system to achieve business goals. The focus areas under Management Infrastructure are performance management, organizational design, capability building, and functional support process.
Mindset and Behaviors
The organizational capability to manage the way people think, feel, and act in the workplace individually as well as collectively. The target areas to focus on here include a compelling purpose, collaborative execution, up-to-date skills, drive to improve, and committed leadership.
Model Warehouse Implementation
Lean Warehousing Transformation necessitates developing a “Model Warehouse,” which presents facilities for supply chain people to practically experience state-of-the-art warehouse operations in a modern warehouse and shop-floor environment. The Model Warehouse incorporates newest technology and systems, and offers real-life conditions for building capabilities—i.e., optimization of storage, pick and pack, and dispatch processes. Newest technologies—e.g., Smart Glasses and HoloLenses—available at the facility help improve the performance of pickers significantly and execute multi-order picking efficiently.
Such a setting allows people to observe and analyze the performance of an exemplary warehouse and implement this knowledge at their own premises. Leading organizations organize a week-long rigorous knowledge sharing workshop—in an experiential learning environment of a Model Warehouse—for their people to have a hands-on experience to learn Lean Warehousing, actual picking, packing, root cause analysis, and performance management. The participants of the Model Warehouse Knowledge Sharing Workshop are excellent candidates for “change agents” to implement Lean Transformation.
Interested in learning more about Lean Warehousing, Model Warehouse Implementation, and Lean Warehousing Transformation? You can download an editable PowerPoint on Lean Warehousing Transformation here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Are you a Management Consultant?
You can download this and hundreds of other consulting frameworks and consulting training guides from the FlevyPro library.
Comments