Editor's Note: If you are interested in becoming an expert on Human Resource Management (HRM), take a look at Flevy's Human Resource Management (HRM) Frameworks offering here. This is a curated collection of best practice frameworks based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. By learning and applying these concepts, you can stay ahead of the curve. Full details here.
Diversity refers to the representation of races, ethnicities, and other minority groups in an organization, or its composition. Inclusion, on the other hand, refers to the degree to which inputs, presence, and perspectives of distinct groups of individuals are valued and their level of integration within a setup.
McKinsey's analysis of the firms it has analyzed since 2014 supports a compelling Business Case for both gender and ethnic/cultural diversity in executive teams.
Despite evidence of a strong rationale for D&I, the majority of businesses fail, in some form, to properly implement D&I. This is irrespective of the type, be they Leaders, Fast Movers, Moderate Movers, Resting on Their Laurels, or Laggards.
Justification for Diversity is growing stronger and clearer, yet despite this, several organizations appear incapable of surmounting significant difficulties in their efforts to make steady and consistent growth.
Implementing a self-assured and structured approach to D&I and pursuing Inclusion with determination is the best way to overcome these barriers.
There are excellent performance opportunities for companies who are prepared to take the initiative and implement the necessary steps to achieve meaningful success on D&I.
Insights from study of Diversity leaders and profound understanding from research and practice on Diversity & Inclusion have helped to determine the successful measures and practices.
Effective D&I measures correspond to a 2-phase strategy comprising of 5 essential steps:
Phase 1: Systematic Business-led Approach to D&I
- Guarantee representation of diverse talent.
- Build up Leadership accountability and aptitude for D&I.
- Facilitate fairness of opportunity.
Phase 2: Bold Steps to Strengthen Inclusion
- Foster openness and confront discrimination.
- Nurture belonging.
Let's go a bit more into a few of the steps.
1. Representation of Diverse Talent
Leaders not only make a business-driven case for D&I reform, but also outline representation goals for themselves. Particularly in executive, line-management, technical, and board positions, great emphasis is placed on recruiting a variety of diverse personnel. In addition to addressing Leadership selection, these measures also address gaps in the organizational hierarchy.
2. Leadership Accountability and Aptitude for D&I
Diversity leaders put their key business executives and managers at the heart of the D&I initiative, which is essential for the formation of an Inclusive culture. Crucial to the positioning of key executives are the organization's inclusive leadership and accountability skills. Both competencies must reach middle management, where D&I is typically relegated when more critical business goals arise. Leaders in Diversity must—and do—go beyond conventional, mechanical, bias training.
3. Fairness of Opportunity via Impartiality & Openness
Equality and fairness of opportunity are crucial factors that must be considered in order to develop Inclusion, hence retaining and expanding Diverse talent. Diversity leaders ensure Opportunity Equality and Fairness with regards to Leadership attitudes, behavior, and skills.
This is ensured through the neutrality of talent acquiring, selection, and retaining, process, particularly in the context of professional advancement and equitable compensation.
Interested in learning more about all the step for D&I Improvement and specific steps by types of D&I companies? You can download an editable PowerPoint presentation on Diversity & Inclusion (D&I) Improvement here on the Flevy documents marketplace.
Want to Achieve Excellence in Human Resource Management (HRM)?
Gain the knowledge and develop the expertise to become an expert in Human Resource Management (HRM). Our frameworks are based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. Click here for full details.
The purpose of Human Resources (HR) is to ensure our organization achieves success through our people. Without the right people in place—at all levels of the organization—we will never be able to execute our Strategy effectively.
This begs the question: Does your organization view HR as a support function or a strategic one? Research shows leading organizations leverage HR as a strategic function, one that both supports and drives the organization's Strategy. In fact, having strong HRM capabilities is a source of Competitive Advantage.
This has never been more true than right now in the Digital Age, as organizations must compete for specialized talent to drive forward their Digital Transformation Strategies. Beyond just hiring and selection, HR also plays the critical role in retaining talent—by keeping people engaged, motivated, and happy.
Learn about our Human Resource Management (HRM) Best Practice Frameworks here.
Do You Find Value in This Framework?
You can download in-depth presentations on this and hundreds of similar business frameworks from the FlevyPro Library. FlevyPro is trusted and utilized by 1000s of management consultants and corporate executives.
For additional best practices available on Flevy, have a look at our top 100 lists:
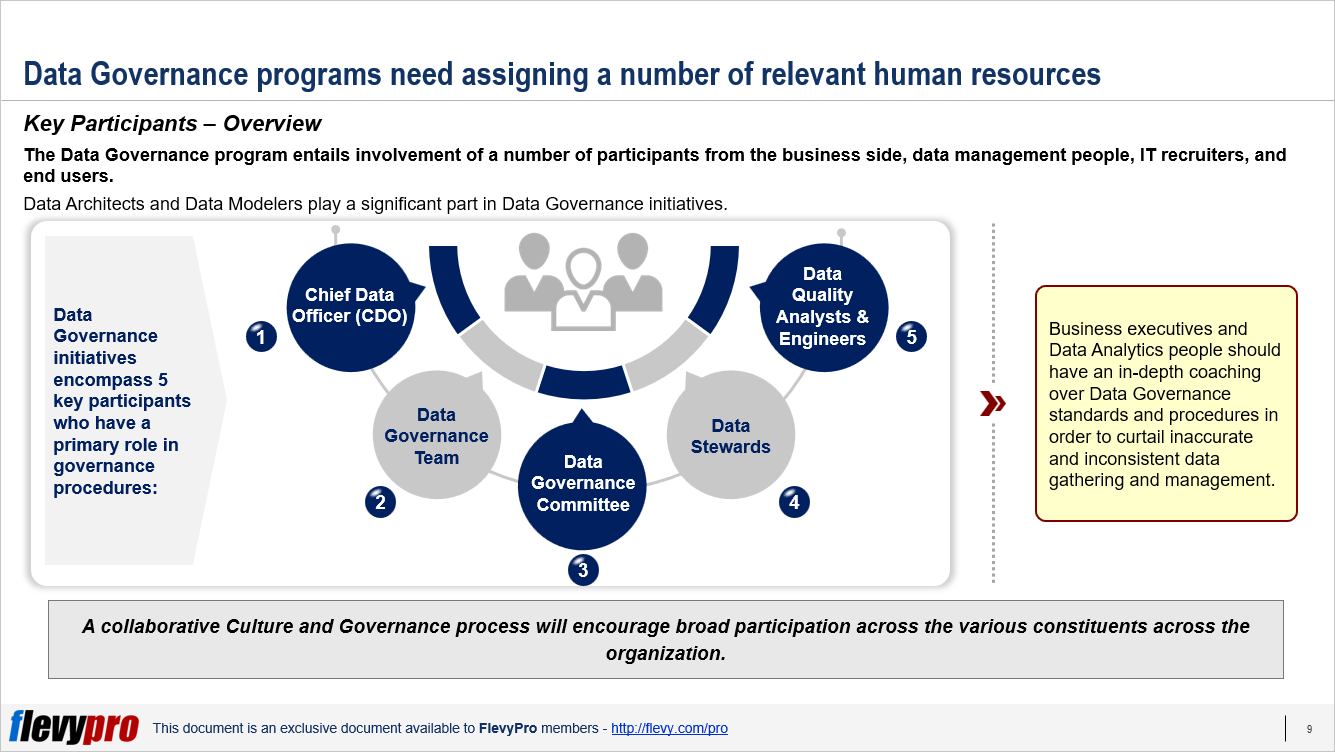
 Data Governance is a set of practices that outline the roles and accountabilities related to data and support the organization’s Business Model by generating and consuming data. It’s all about overseeing the accessibility, practicality, reliability and safety of enterprise data.
Data Governance is a set of practices that outline the roles and accountabilities related to data and support the organization’s Business Model by generating and consuming data. It’s all about overseeing the accessibility, practicality, reliability and safety of enterprise data.